The RoboClaw has several useful control methods, one of them being analog control. With analog control you can use a variety of user interface options so long as they output an appropriate analog voltage. In this Application Note we’ll be using an analog joystick to control two motors with the RoboClaw in analog mode.
Motor controller like the RoboClaw used feedback from sensors like encoders to maintain the speed and position of motors. Internally, a system called a PID controller is used to maintain these values at their given setpoints. In this App Note we’ll be looking at the what, why and how of a PID controller.
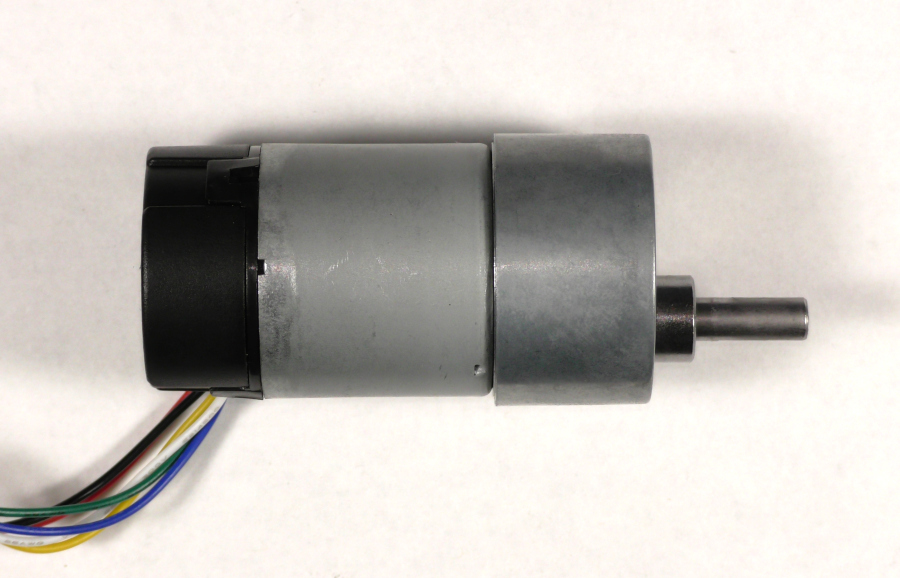
Encoders allow the RoboClaw to provide accurate and consistent speed and position control of motors. In this Application Note we’ll be wiring a common motor and encoder combination to the RoboClaw.
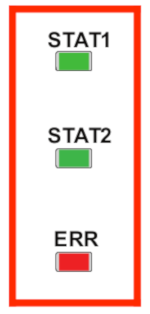
Things don’t always go as planned when operating your robots and problems can occur that need to be dealt with as they come up. Thankfully, the RobClaw motor controller has a handy set of features that alerts you to problems that may crop up. We’ll be looking in to how to read the error messages of the RoboClaw via the onboard leds and how to diagnose the problems they are associated it.
Selecting a battery for your robotics projects is vital in ensuring your robot will have the power and endurance you’re looking for. There are several properties of batteries you’ll need to be aware of make the right choice for your project. After reading this App Note you’ll be informed enough to make the right decision.